Mediastinal tumors (Mediastinaltumoren)
General information:
Clasically the mediastinum is divided into 3 parts:
- Anterior mediastinum: from the posteriour surface of the sternum to the anterior surface of the great vessels, heart and pericardium to the thoracic inlet. In this space the thymus is located. Thymoma is a reare lesion in children (occasionally associated with myasthenia gravis). Maglinant thymomas (epithelial nature) need aggressive resection (limited response to radio- and chemotherapy). Other tumors: Teratomas (mixed cystic an solid components).
- Middle mediastinum: contains the heart, trachea, bronchi, great vessels, esophagus, the lymphatic tissue. Masses are likely to be caused by the lymphoid tissue located around the lung hilus (inflammatory lesions, Non-Hodgkin lymphomas or Hodgkin disease).
- Posterior mediastiunum: Mainly the paravertebral sulcus. Masses are most commonly benign ganglioneuromas (in older children and teenagers, frequently asymptomatic), benign neurofibromas (dumbbell tumor, M. Recklinghausen) and malignant neuroblastomas (better prognosisis: under 1 year of age). The neurogenic tumors have their origin from the sympathetic chain. Rare lesions: anterior thoracic meningocele, neureneteric cysts (failure of separation of the notochord and foregut).
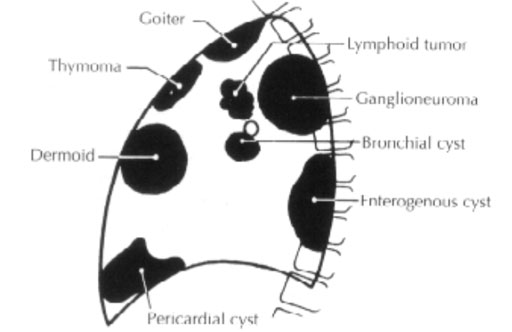
Mediastinal masses (Carachi R. Et. al.: The Surgery of Childhood Tumors)
Symptoms:
- Respiratory distress due to compression of the airways (cough, wheezing, recurrent respiratory infections, atelectasis, haemoptysis).
- Dysphagia (compression of the oesophagus).
- Hoarseness (compression of the laryngeal nerve).
Diagnostic workout:
- Plain thoracic X-ray, CT (to detect calcifications) and MRI (spinal involvement).
- CT guided puncture of the mass (histology).
- Bronchoscopy with transbronchial needle aspiration (cytology).
- Thoracoscopy as a minimal invasive procedure or throracotomy to take larger biopsies.
- Tumor markers: alpha - 1 - fetoprotein and beta - HCG (teratomas).
- In lymphomas: bone marrow puncture.
Indication for operation:
- Because of diagnostically and therapeutically reasons.
Treatment/Operation:
- During anaesthesia induction ventilation problems may occur (risk of respiratory collapse in relation to the size of the mediastinal mass).
- Median sternotomy (sternal splitting incision) for lesions in the anterior mediastinum.
- Lateral thoracotomy to reach the middle and posterior mediastinum.
- Pay attention to the phrenic nerve the vagus nerve and the recurrent laryngeal nerve.
- Thoracoscopically performed minimally invasive resections (biopsy, complete resection: thymoma, lymphatic nodes, neurogenic tumors).
Postoperative management:
- Mediastinal tube drainage.
Prognosis:
- Depends on the diagnosis and the stage of the disease.



