Lung tumors
(Lungentumore im Kindes- und Jugendalter)
- Metastases (Wilms tumor, neuroblastoma, ...).
- Pleuropulmonary blastoma (PPB): rare and highly aggressive malignant tumor of the lung. 25% are extrapulmonary. Metastases are usually found in the central nervous system. The tumor may be associated with CCAM.
- The tumor arises from the lung or the pleura or both sites.
- There seems to be a constitutional and heritable predisposition to other dysplastic and neoplastic diseases (cystic nephroma, pulmonary cysts) in 25% of these patients. The families should be investigated carefully.
- Bilateral PPB has been described.
- Poor prognosis.
- Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma is also very rare. 35% arise from pre-existing pulmonary cystic malformations (CCAM).
- Bronchial carcinoid.
- Bronchial mucoepidermoid tumors.
- Inflammatory pseudo-tumor (synonyms: plasma cell granuloma, histiocytoma, fibrous xanthoma).
- Suspected aetiology: uncontrolled reaction to tissue damage or chronic inflammation.
- 50% of patients under the age of 16.
- 40% without any symptoms.
- Symptoms: cough, fever, wheezing, fatigue, lower respiratory tract infection.
- Histologically: spindle cells, myofibroblasts, granulomatous inflammation, lymphoid hyperplasia, fibrosis.
- Invasive growth (vascular invasion, bone destruction) recurrence and metastases can occur.
- Needle biopsy may lead to an unclear diagnosis. Surgery is mandatory.
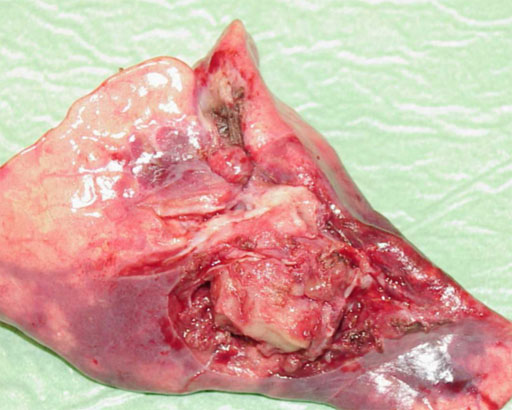
Inflammatory pseudo-tumor surrounding the main bronchus



